The Versatile Strength of Concrete Slabs: Foundations, Construction, and Beyond
Understanding Concrete Slabs
Concrete slabs are an integral component of modern construction, serving as the foundation for buildings, roads, and various infrastructure projects. These slabs are flat, horizontal surfaces made from a mixture of cement, water, sand, and gravel, which hardens over time to form a solid, durable structure. The importance of concrete slabs in construction cannot be overstated, as they provide stability and support for structures, ensuring safety and longevity.
One of the primary reasons concrete slabs are so widely used is their versatility. They can be customized to fit various shapes and sizes, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Whether it’s a residential home, a commercial building, or a public infrastructure project, concrete slabs can be adapted to meet specific requirements. Additionally, they are known for their strength and durability, capable of withstanding heavy loads and adverse weather conditions.
Types of Concrete Slabs
Concrete slabs come in various types, each designed for specific purposes and conditions. The most common types include:
- On-grade slabs: These are constructed directly on the ground and are commonly used for driveways, sidewalks, and patios.
- Suspended slabs: These are elevated above the ground and supported by columns or walls, often used in multi-story buildings.
- Pre-stressed slabs: Reinforced with steel cables or rods, these slabs offer enhanced strength and are used in bridges and high-rise structures.
The choice of slab type depends on factors such as the load it needs to bear, the soil conditions, and the specific requirements of the project. Understanding these types helps builders and engineers select the appropriate slab for their needs, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Construction and Installation
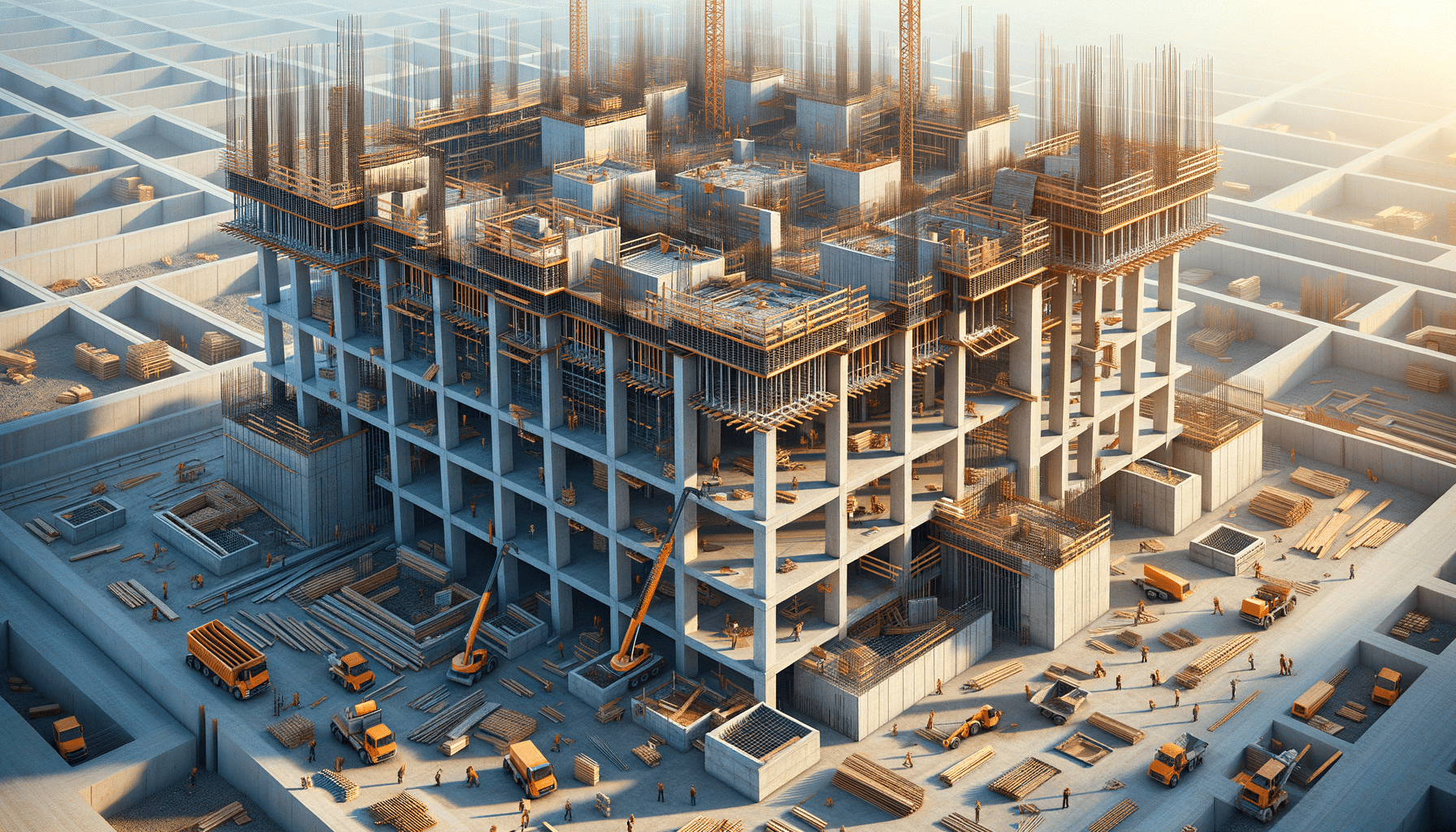
The construction of concrete slabs involves several key steps, each crucial to the final product’s quality and durability. The process begins with site preparation, which includes clearing the area, leveling the ground, and setting up forms to contain the concrete. Proper preparation is essential to prevent issues such as cracking or uneven settling.
Once the site is prepared, the concrete mixture is poured into the forms. This step requires precision and expertise to ensure the mixture is evenly distributed and free of air pockets. After pouring, the concrete is leveled and smoothed using tools such as screeds and trowels. The curing process follows, during which the concrete hardens and gains strength over time. Proper curing is vital to achieving the desired durability and longevity of the slab.
Advantages of Concrete Slabs
Concrete slabs offer numerous advantages that make them a preferred choice in construction. Some of these benefits include:
- Durability: Concrete is known for its long-lasting nature, capable of withstanding heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions.
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to other building materials, concrete is relatively affordable, offering excellent value for money.
- Fire resistance: Concrete slabs provide a high level of fire resistance, enhancing the safety of structures.
- Energy efficiency: Concrete’s thermal mass helps regulate indoor temperatures, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling.
These advantages make concrete slabs an attractive option for builders and developers, contributing to the widespread use of this material in various construction projects.
Challenges and Considerations
While concrete slabs offer many benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind. One of the primary challenges is the potential for cracking, which can occur due to factors such as improper curing, temperature fluctuations, or soil movement. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to follow best practices in construction and maintenance.
Another consideration is the environmental impact of concrete production. The manufacturing process involves significant energy consumption and carbon emissions, prompting the industry to explore more sustainable practices and materials. Innovations such as recycled aggregates and alternative cement types are being developed to reduce the environmental footprint of concrete slabs.
Conclusion
Concrete slabs are a cornerstone of modern construction, offering strength, durability, and versatility in a wide range of applications. From residential homes to large infrastructure projects, these slabs provide a reliable foundation that supports the safety and longevity of structures. By understanding the types, construction processes, and benefits of concrete slabs, builders and developers can make informed decisions that enhance the quality and sustainability of their projects.