Gaining Proficiency in Concrete Crack Repair Techniques
Introduction to Concrete Crack Repair
Concrete is a widely used material in construction due to its durability and strength. However, over time, even the most robust concrete structures can develop cracks due to various factors such as temperature changes, structural loads, or shrinkage. Understanding and applying effective concrete crack repair techniques is essential for maintaining the integrity and appearance of these structures. In this section, we will explore the importance of addressing concrete cracks, the common causes, and the initial steps to take when dealing with these issues.
Cracks in concrete can compromise the structural integrity of buildings, roads, and other infrastructures. They can also lead to further deterioration if not addressed promptly. The primary causes of concrete cracking include thermal expansion and contraction, drying shrinkage, and ground settlement. Identifying the root cause of the cracking is crucial in selecting the appropriate repair method. Initial steps in concrete crack repair involve assessing the extent and type of cracking, determining the underlying cause, and selecting the most suitable repair technique.
Types of Concrete Cracks and Their Causes
Concrete cracks can be categorized into several types, each with different characteristics and causes. Understanding these types is vital for selecting the appropriate repair method. The most common types of concrete cracks include:
- Plastic Shrinkage Cracks: These occur when the surface of the concrete dries too quickly, causing the top layer to shrink and crack. This typically happens in hot, windy weather.
- Settlement Cracks: These occur when the ground beneath the concrete settles unevenly, leading to cracks that can vary in size and shape.
- Thermal Cracks: Resulting from temperature variations, these cracks occur when the concrete expands and contracts with changes in temperature.
- Structural Cracks: These are often caused by excessive loads or inadequate support, leading to significant structural damage.
Each type of crack requires a specific approach to repair, and understanding their distinct causes helps in choosing the right technique. For instance, plastic shrinkage cracks might be addressed by improving curing conditions, while structural cracks may need reinforcement or additional support.
Common Concrete Crack Repair Techniques
Once the type and cause of the concrete crack have been identified, the next step is to choose the appropriate repair technique. Here are some of the most common methods used in concrete crack repair:
- Epoxy Injection: This method is suitable for repairing small cracks and restoring structural integrity. Epoxy is injected into the cracks, bonding the concrete together and preventing further movement.
- Routing and Sealing: Ideal for non-structural cracks, this technique involves enlarging the crack and filling it with a sealant to prevent water infiltration and further deterioration.
- Stitching: This involves drilling holes on both sides of the crack and installing metal staples or stitching dogs to hold the concrete together.
- Overlay: A thin layer of new concrete is applied over the cracked surface to provide a fresh and durable finish.
Each technique has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on factors such as the crack’s size, location, and the structure’s intended use. For instance, epoxy injection is highly effective for structural repairs but may not be suitable for cracks exposed to constant moisture.
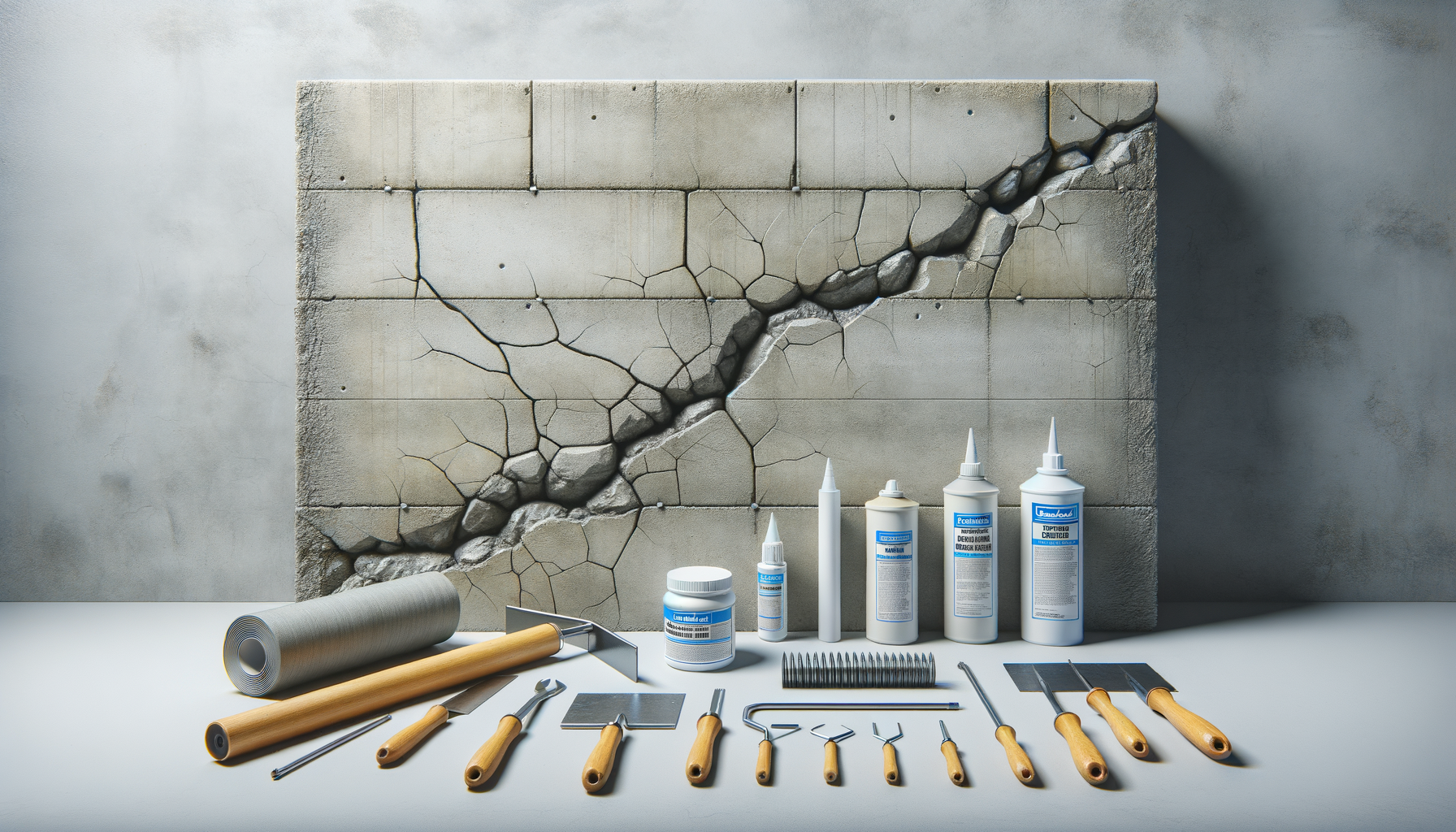
Tools and Materials for Concrete Crack Repair
Successful concrete crack repair requires the right tools and materials. The selection of these resources is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of the repair. Here is a list of essential tools and materials commonly used in concrete crack repair:
- Epoxy or Polyurethane Resins: These materials are used for injection techniques to bond and seal cracks.
- Sealants: Various sealants are available for filling and sealing cracks, including silicone and acrylic-based products.
- Concrete Mix: For overlays and larger repairs, a quality concrete mix is necessary to ensure a durable finish.
- Chisels and Hammers: These tools are used for routing and preparing cracks before applying repair materials.
- Injection Pumps: Specialized pumps are required for injecting epoxy or polyurethane into cracks.
Choosing the right tools and materials is essential for achieving a successful repair. It’s important to consider factors such as the crack’s size, location, and environmental conditions when selecting these resources. Proper preparation and application techniques are also critical to ensure the repair’s durability and effectiveness.
Conclusion: Maintaining Concrete Structures
Concrete crack repair is a vital aspect of maintaining the safety, functionality, and aesthetics of concrete structures. By understanding the types of cracks, their causes, and the appropriate repair techniques, property owners and maintenance professionals can effectively address these issues and prolong the lifespan of their concrete assets.
Regular inspections and timely repairs are crucial in preventing minor cracks from developing into major structural problems. Investing in quality materials and employing skilled professionals can make a significant difference in the success of concrete crack repairs. By taking a proactive approach, you can ensure the longevity and durability of your concrete structures, ultimately saving time and resources in the long run.